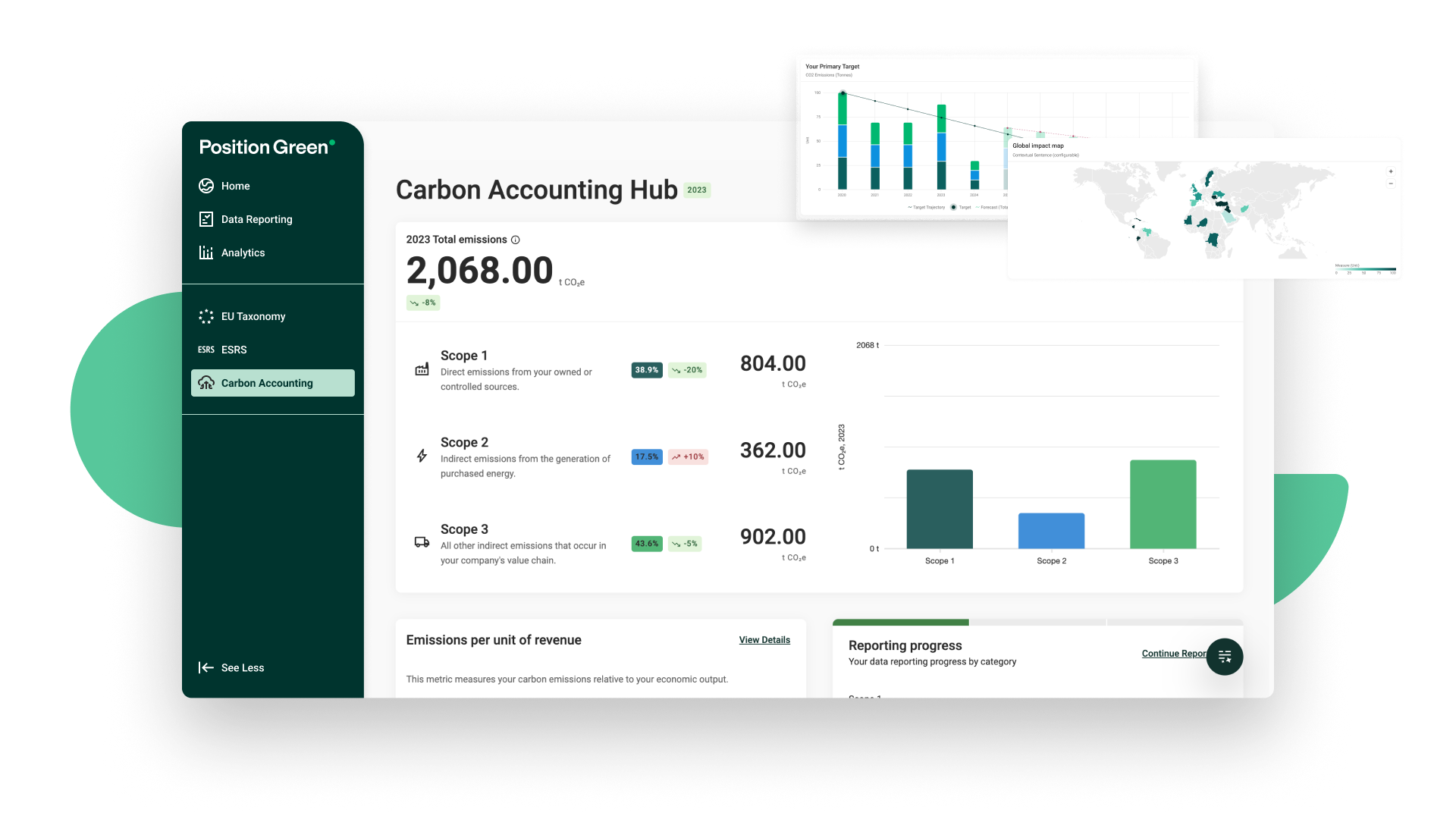
The Greenhouse Gas Protocol is an organisation that provides the world’s most widely used global standards for carbon accounting and reporting, for both public and private sectors. It outlines how businesses can define organisational boundaries for GHG reporting and introduced the division of emissions into Scope 1, 2 and 3 to provide a clear overview of where a company’s emissions are occurring in its operations and its wider value chain. GHG Protocol serves to provide guidelines on what to report on, how the reporting should be done, and how data and emission factors can be collected and used.
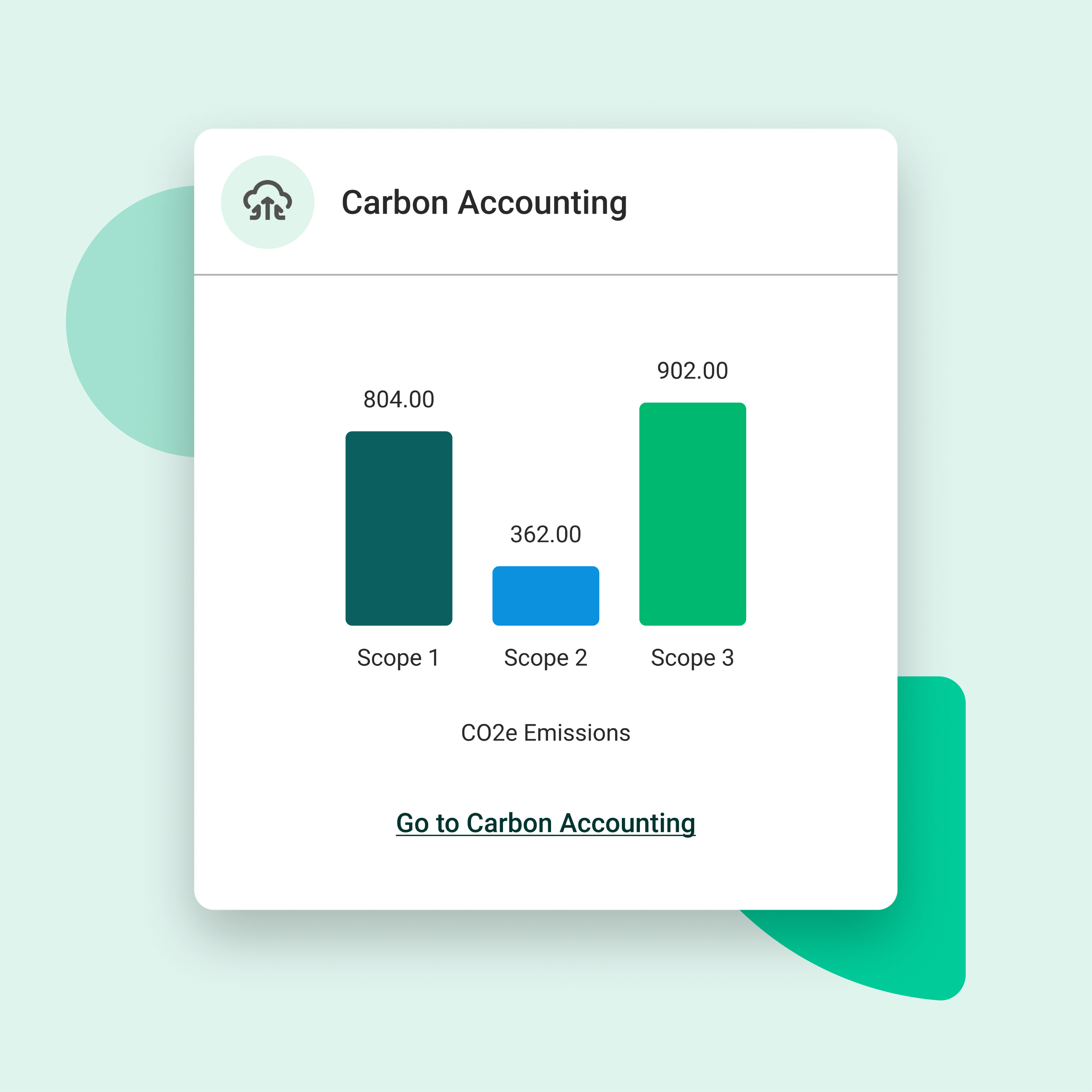
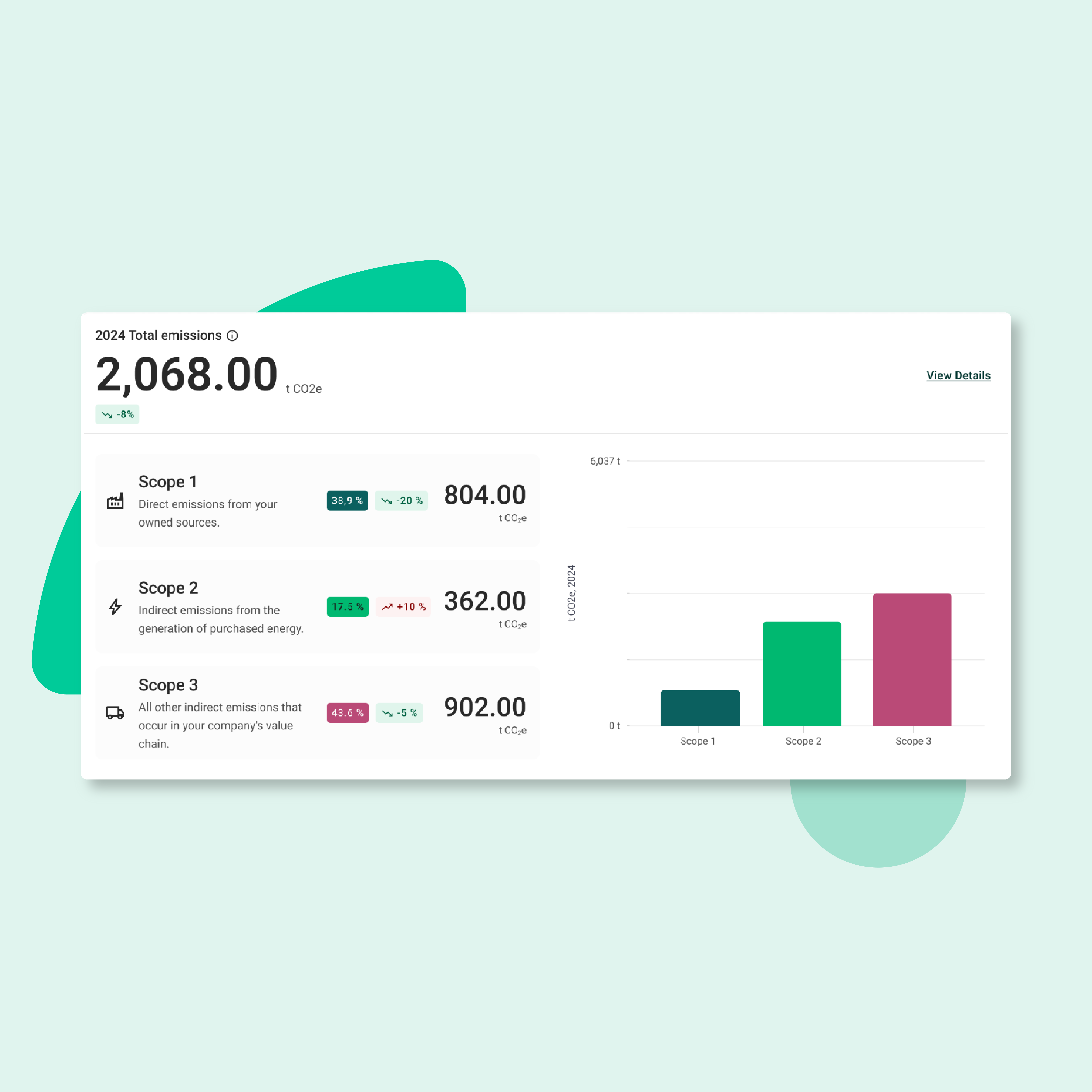
Scope 1: direct GHG emissions from sources owned or controlled by the organisation, such as on-site fuel combustion and process emissions, directly contributing to its carbon footprint.
Scope 2: indirect GHG emissions from the generation of electricity, steam, heating and cooling, that is purchased and used by the organisation.
Scope 3: other indirect GHG emissions, occurring from sources not owned or controlled by the organisation but by those that it’s indirectly responsible for up and down its value chain, for example, when we buy, use and dispose of products from suppliers.